What is CAPA in the Pharmaceutical Industry?
Product quality is a key factor for any pharmaceutical organization and the CAPA process helps ensure that the products are of high quality.
The CAPA process plays an important role in the quality management system of any pharmaceutical company. It helps to identify, evaluate, prioritize and manage nonconformities or problems related to products or processes to prevent them from recurring.
What is CAPA?
CAPA stands for Corrective Action and Preventive Action, a system for analyzing, correcting, and preventing issues. It outlines procedures to solve the issue, it also analyzes the cause of the problem to prevent its recurrence.
For example, Corrective Action and Preventive Action (CAPA) can investigate the misprinting problem in a pharmaceutical manufacturing environment. The CAPA initially proposes corrective actions to solve the misprinting problem and then investigates the cause to prevent recurrence in the future.
What Should Trigger CAPA?
Not every deviation or nonconformance requires a CAPA.
An unnecessary CAPA can result in additional costs, processes slowdowns, and inefficient usage of the organization’s resources. It also becomes difficult for the team to follow up, resulting in an uncompleted pile of CAPA’s.
Conversely, uncompleted CAPA’s can be a serious compliance problem.
Certain Situations that Can Trigger a CAPA
Nonconformances or Deviations
Non-conformance is the failure to fulfill the associated requirements and can occur both in products and processes. Non-conformance can also result due to an inability to meet the requirements of a customer. It can be identified during the manufacturing process or if a defective product is returned to the manufacturer.
For example, manufacturing requires a specific temperature for carrying out a specific process. However, quality personnel detects the temperature deviation and find out that this deviation is occurring for a very long time. This problem is a non-conformity and triggers a CAPA.
What Is Non-Conformance And How to Minimize It
Customer Complaints
Customer complaints help identify product deficiencies after it is released to the market.
The communication mode can be written, oral, or electronic. The defect can indicate a product’s inability to fulfill its desired effectiveness, quality, results, or performance.
Every manufacturer must maintain a complaint handling system for receiving, reviewing, and evaluating complaints. The manufacturer is also responsible for processing the complaints promptly, documenting complaint reviews and investigations as well as sharing information across relevant departments and regulatory bodies.
For instance, if a pharmaceutical manufacturer receives a complaint of an empty pocket in a tablet blister pack, it should trigger a CAPA.
Audit Findings
The main objective of the pharmaceutical audits is to inspect whether the existing quality system is in line with the established quality system requirements.
There are two types of audits – internal and external audits.
Internal audit is performed by a team of the same manufacturing organization. However, they must be from another department and should not be interested in the department being audited.
On the other hand, external regulatory and standardization organizations perform external audits.
For example, if during an audit, particles are found in injectables filling operation, it will result in non-conformance. Since this is a serious issue, it would require a CAPA.
Using an efficient CAPA management software like SimpleQMS you can quickly initiate forms from various deviations, non-conformances, customer complaints, audit findings, and other issues.
The Importance of a CAPA Process in the Pharmaceutical Industry
CAPA is a resource-intensive activity, and as we discuss, in some cases it can be considered unnecessary.
However, a properly established CAPA process can be an excellent tool for achieving an organization’s quality goals in the following manner.
Regulatory Compliance
CAPA is a compliance requirement for different regulatory agencies,such as the FDA. For example, if during the FDA inspection an auditor finds any cGMP violations, the accredited manufacturers should implement appropriate Corrective Actions and Preventive Actions (CAPA’s). The FDA issues the warning letter if the pharma manufacturer fails to execute necessary Corrective Actions and Preventive Actions (CAPA’s).
Proper CAPA process in a pharmaceutical’s maintenance department can help to keep their maintenance strategies, process flow, and documentation procedures according to guidelines of standardization bodies.
Successful Audits
cGMP violations in pharma manufacturing are not uncommon and can occur due to reasons such as Human Negligence and Environmental factors. During their audit and inspection, Regulatory bodies pay special attention to the organization’s approach towards mitigating risks and improving quality throughout the entire product life cycle. One of many ways is the implementation of a proper CAPA system.
Executing the Corrective Actions and Preventive Actions (CAPA’s) on time helps keep the organization audit-ready. The CAPA must be appropriately carried out, documented, maintained, and produced at the time of audits and inspections.
Cost Savings
One of the main advantages of CAPA is cost-saving, resulting in efficient output with optimum quality.
It also creates reliability in their processes, systems, and products, which could result in increased revenue for a pharmaceutical manufacturer.
In the beginning, it might be costly to establish a CAPA process, but as time advances and the process itself improves, it eliminates the recurring problem and results in improved process performance with minimum downtime and reduced failures.
Overall Efficiency
CAPA increases the efficiency of the processes and systems, as an effective CAPA reduces overall operational costs. The cost-saving can then help promote innovation and improvement in the product.
Improved efficiency can also increase market share by offering cost-effective, quality products to compete with the competitors.
One effective way of improving cost and efficiency is using a digital CAPA management software solution. With SimplerQMS CAPA software, personnel is more focused on executing the process rather than planning, following up, and preparing for audits and inspections.
Improved Product Quality
CAPA is a process improvement system that increases product quality. It includes identifying and investigating product problems and obliging manufacturers to prevent their recurrence. It also enables the manufacturer to study the implemented action plan’s effects and monitor the effectiveness of proposed corrective and preventive actions.
If these activities are carried out regularly, it significantly increases the product quality and lowers product failure.
CAPA Requirements
Let’s look at some of the regulatory requirements regarding CAPA.
ICH Q10
ICH Q10 is harmonized model for pharma manufacturers to implement a Quality System. It is based on existing models such as cGMP and does not create an alternate model regarding quality requirements. The ICH Q10 considers CAPA as one of four Pharmaceutical Quality System elements.
The ICH Q10 requires the pharma manufacturers to implement a CAPA system for handling complaints, product rejections, nonconformances, and recalls.
The FDA cGMP requirements can be summarized below:
CAPA procedures must be well-defined and documented
Appropriate sources of product and quality problems must be identified
Product and quality information that may show unfavorable trends should be identified
It is important to verify that the data received by the CAPA system are complete, accurate, and timely
You must verify that appropriate statistical methods are employed (where necessary) to detect recurring quality problems
Failure investigation procedures must be followed
Appropriate actions should be taken for significant product and quality problems identification from data sources
Corrective and preventive actions should be effective and verified or validated before implementation
You must verify that corrective and preventive actions for product and quality problems are implemented and documented. Information regarding nonconforming product and quality problems and corrective and preventive actions must be properly disseminated, including dissemination for management review
ISO 9000:2015
The ISO is a standardization body that develops standards, including the Quality Management System (QMS). The QMS focuses on product quality, and the CAPA is a module within a comprehensive QMS.
According to ISO 9000:2015, the pharmaceutical manufacturer is responsible for taking action and controlling the nonconformities. It also requires the manufacturer to eliminate the cause of the nonconformity by:
Reviewing and analyzing the nonconformity;
Determining the causes of the nonconformity;
Determining if similar nonconformities exist, or could potentially occur;
Similar to the FDA requirements, the manufacturer is responsible for implementing corrective actions, reviewing the effectiveness of disciplinary action, analyzing risks and opportunities, and any change for process improvement.
Moreover, the manufacturer should always retain documented evidence of non-conformities and corrective actions.
Steps of CAPA Process
Let’s go through the seven steps of a CAPA implementation process.
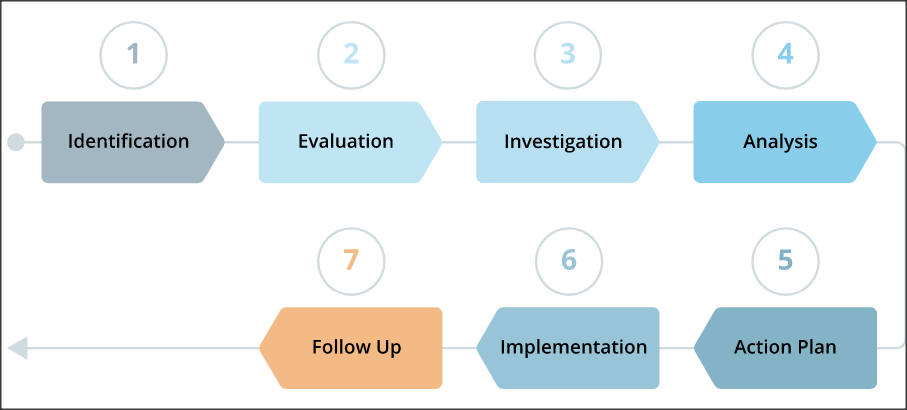
Identification
Problem identification is the first step and plays a vital role in the success of the ongoing CAPA process. It includes identifying all the product and quality problems that require corrective actions. It also provides identification of sources used to classify issues such as complaints, returned product records, quality audits, installation reports, lawsuits, and non-conforming products.
Evaluation
In this stage, the problem is evaluated for further decision-making.
The problem is analyzed to determine its nature and whether it requires a CAPA or not? It also considers its impact on other processes and its effect on the output.
It also analyzes the severity of the problem.
For example, suppose a lack of safety is identified on the machine during an audit. In that case, it can be evaluated for different severity levels and how it impacts the machine operation and operator safety.
Investigation
In this step, the problem is investigated for further planning.
The typical investigation includes objectives, i.e., deliverables, Procedures delivering the intent of the action, and Personnel for conducting the investigation. The root cause should be documented for better understanding and implementation.
For example, a team leader’s responsibilities can include authorization to use departmental resources and interviewing the concerned personnel to fully understand the problem.
Analysis
This step identifies and establishes the root cause of the problem by investigating the available data. The required information must be accurately depicted and preserved to reflect the actual cause of the problem.
For example, if a misprint is detected on any pharmaceutical product, the analysis would focus on answering the following questions:
What are the contributing factors to the problem?
Is the printing system reliable?
Or is the operator capable enough to qualify for system operation?
Action Plan
This step’s success depends on the success of the preceding steps.
It is a series of steps required to implement corrective and preventive actions.
For example, it might include employee training if the CAPA team concludes that the cause of the problem was the inability of the personnel to use the system.
Implementation
It is about how the action plan is implemented, devised in the previous stage.
It includes detailed information about the action plan, desired outcomes, settings, steps, and observation. The final action plan must be thoroughly documented for record purposes.
For example, if the training plan is the action plan, implementation of the training could include devising training contents, arranging training resources, instructor, and so on.
Follow Up
After the team executes the CAPA activity, they must follow up.
It helps to measure the effectiveness of the Corrective and Preventive actions and improves the remedial measures.
After this stage, the CAPA activity is finally concluded with a detailed CAPA report.
For example, the training plan is the suggested solution. In that case, follow-up could include assessing the participant’s capabilities, whether more training is required or not, and marking participants as pass or fail.
Using QMS software with a built-in training management software solution you can assure efficient, well-documented, and compliant training management. With SimplerQMS, you can ensure that all employees receive the correct training based on their functional roles. Automatic notifications and reminders ensure that everyone is kept up to date with new trainable procedures, instructions, documents, and videos.
Common Challenges With CAPA
Many pharmaceutical manufacturers face challenges when implementing Corrective Actions and Preventive Actions (CAPA’s).
Because every manufacturer wants to focus on production, and during production, cGMP violations are not uncommon. These violations demand Corrective and Preventive Actions, thus most manufacturers found CAPA one of the primary compliance pain points.
In-Efficient Root Cause Analysis
The CAPA is all about Root Cause Analysis (RCA) to investigate and pinpoint the problem cause. If it does not process in the right direction, the entire CAPA will have inefficient solutions and wastage of resources. It could result in corrective actions that address the same event repeatedly.
There are many reasons for an inefficient Root Cause Analysis (RCA), for example:
The inability of the CAPA team to identify, and categorize the problem
Lack of a tool for CAPA processing like CAPA management software
Not giving importance to RCA and instead of treating it as a compliance requirement
Manual CAPA Processing
Most pharma manufacturers still use manual paper/spreadsheet-based systems to process their CAPA’s. This creates challenges for pharma manufacturers to maintain consistency and comply with the regulatory requirements regarding a CAPA system.
Without a dedicated document control solution, pharma manufacturers can face de-centralized documents, manual chasing for signatures, overlapping responsibilities, and most importantly, missing due dates in implementing CAPA.
This can also result in overused CAPA or underused CAPA. This means initiating CAPA for the issues that do not require CAPA while missing the critical conformities requiring corrective and preventive actions.
Typical CAPA form includes:
Detailed problem description
Root Cause associated with the problem
Corrective actions proposed to solve the problem
Preventive actions proposed to prevent recurring
Approval and Signatures from the concerned department, and personnel involved in the CAPA process
Keep Data Centralized
Secure data storage, access controls are key to any process, and timely data availability is vital to the success of any CAPA activity.
Therefore, it is recommended to consider implementing a document control software system like SimplerQMS that stores the data in centralized and secure cloud storage and makes it readily available at any time, from anywhere.
Document Non-Conformities and Feedback
Recording all non-conformities and feedback helps CAPA keep on track, in line with main objectives. Because, during CAPA, there can be many input variables which can be sometimes relevant, and sometimes not. Recording all the information makes it possible to analyze during the decision-making step.
For example, the information required during the identification stage should be thoroughly filled, including problems and their sources.
Risk-Based Approach
It is recommended to execute CAPA by utilizing a risk-based approach. The risk-based approach allows assessing risks associated with non-conformity under observation. The outcome of the CAPA is treated as a risk, with its appropriate severity level.
For example, if a department fails to show a control copy of the Job Description for any of its personnel, this shortcoming can be categorized as Low, Medium, or High risk, according to the acceptance criteria.
Simple Problem Definition
Problem definition or presentation should be simple, aimed at ordinary personnel with basic process understanding.
This helps to quickly and easily understand the problem without confusion. Simple problem definition leads to effective and accurate solutions, resulting in better process improvement and quality.
Digitizing CAPA Management Processes
Manual, paper-based documentation processes have several drawbacks, including a lack of visibility, incomplete documents, missing signatures, and so on.
Modern eQMS solution with powerful CAPA management capabilities like SimplerQMS allows you to digitize and automate a bulk of routine CAPA processes in a pharmaceutical organization. Such as document routing, notifications, task reminders, escalation, and approvals. This allows you to accelerate issue resolution and ensure regulatory compliance.
by


